
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Building information models (BIMs) are files (often but not always in proprietary formats and containing proprietary data) which can be exchanged or networked to support decision-making about a place. Current building information modeling software is used by individuals, businesses and government agencies who plan, design, construct, operate and maintain diverse physical infrastructures, such as water, waste-water, electricity, gas, refuse and communication utilities, roads, bridges and ports, houses, apartments, schools and shops, offices, factories, warehouses and prisons.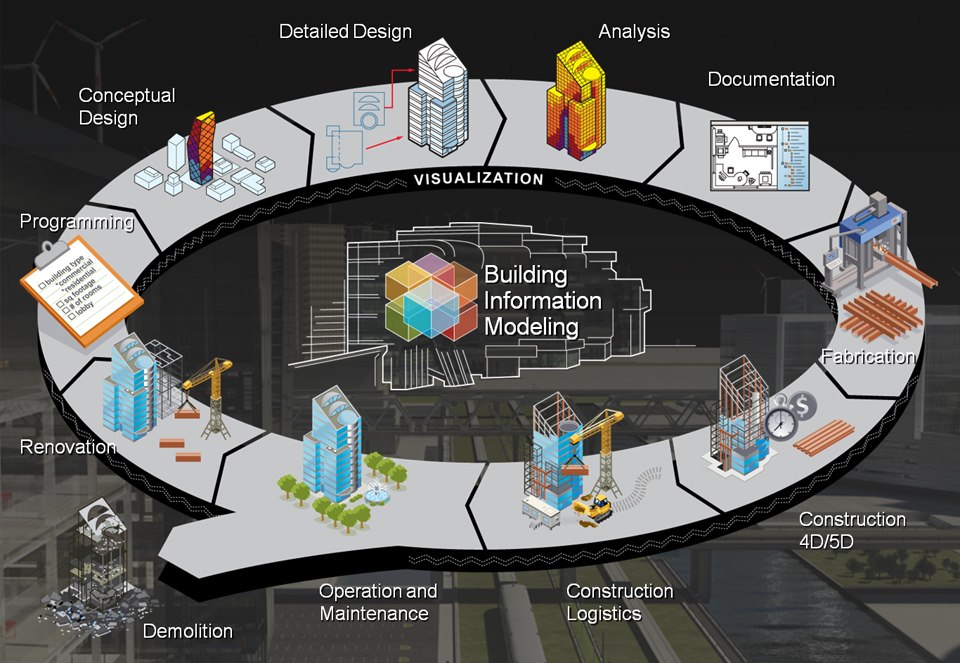
The first software tools developed for modelling buildings emerged in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and included workstation products such as Chuck Eastman’s Building Description System and GLIDE, RUCAPS, Sonata and Reflex. The early applications, and the hardware needed to run them, were expensive, which limited widespread adoption. ArchiCAD’s Radar CH, released in 1984 was the first modelling software made available on a personal computer.
Image Source : https://google.com
Content Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Building_information_modeling
Video Source: https://Youtube.com



